In our increasingly interconnected world, the language interpretation industry plays a pivotal role in breaking down linguistic barriers and facilitating communication. As businesses, organizations, and individuals engage with a diverse global audience, language interpretation has become more critical than ever. In this article, we delve into the trends shaping the industry, the challenges it faces, and best practices to ensure efficient language interpretation services.
Trends Shaping the Language Interpretation Industry
1. Technology Integration
Technology is redefining how language interpretation is delivered. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Translation (MT) tools is rapidly transforming the landscape. AI-powered language interpretation applications, like chatbots and virtual assistants, are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering real-time translation services. The flip side of AI unfortunately has limitations too.
2. Remote Interpretation Services
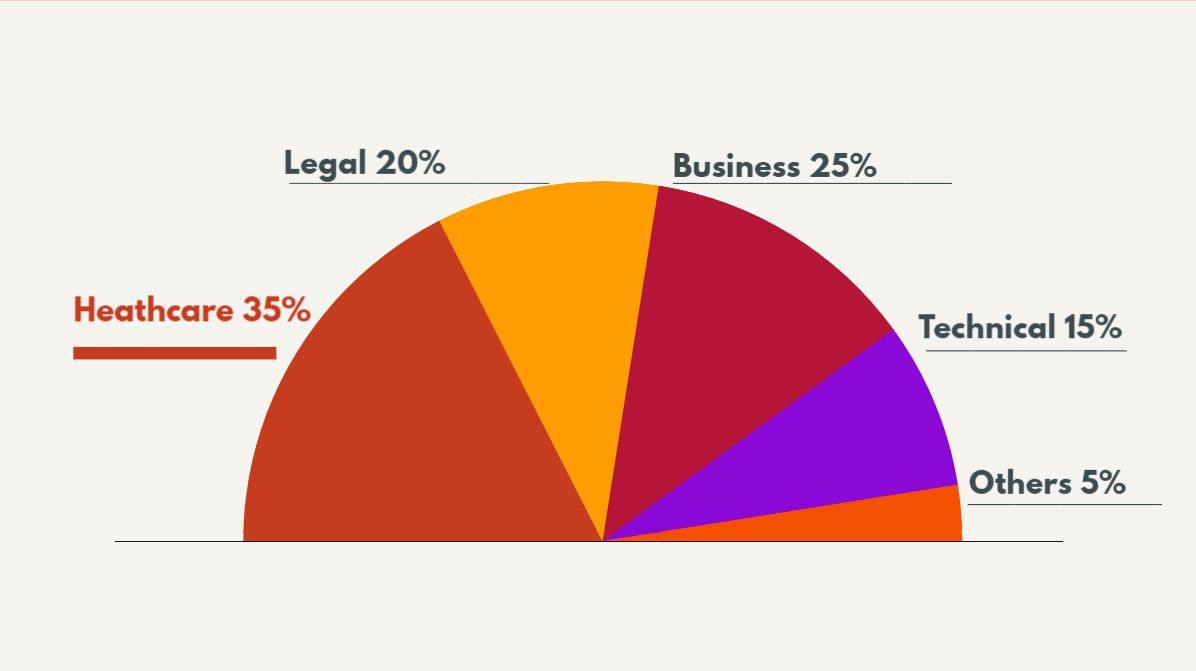
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote interpretation services. Video conferencing platforms and telehealth services witnessed a surge in demand, driving the need for remote interpreters. This trend is likely to persist as it offers cost-effective and convenient solutions, especially in healthcare, legal, and business settings.
3. Specialisation and Niche Services
Language interpreters are increasingly specialising in specific fields, such as medical, legal, or technical interpretation. This specialisation ensures greater accuracy and understanding within complex domains. As industries demand more precision, interpreters with expertise in these niches are highly sought after.
Challenges in the Language Interpretation Industry
1. Quality Assurance in Technology-Driven Interpretation
While technology has brought significant advancements, maintaining quality and accuracy remains a challenge. AI and MT tools may struggle with context, nuances, and cultural intricacies that human interpreters excel. Instances of misinterpretation can have severe consequences, emphasizing the need for human oversight and quality control.
2. Cultural Sensitivity and Nuance
Language interpretation extends beyond words; it encompasses cultural nuances, idiomatic expressions, and non-verbal cues. Interpreters must be culturally sensitive to ensure effective communication. Misunderstanding cultural contexts can lead to confusion or offense, making cultural competence a crucial skill for interpreters.
3. Data Security and Privacy
In an age where information is shared across borders, data security and privacy concerns are paramount. Remote interpretation services, in particular, must adhere to stringent security measures to protect sensitive information. Breaches in confidentiality can result in legal and reputational consequences.
Conclusion
The language interpretation industry is undergoing a profound transformation driven by technology, specialization, and the need for seamless communication. While these trends offer new opportunities, they also present challenges related to quality, cultural sensitivity, and data security. Adhering to best practices, such as a hybrid approach, continuous training, and effective communication, can help mitigate these challenges and ensure that language interpretation continues to play a vital role in our globalized world. As we navigate this dynamic landscape, staying informed about trends and embracing best practices remains paramount for both interpreters and their clients.



